By Somini Sengupta and
-
- 196
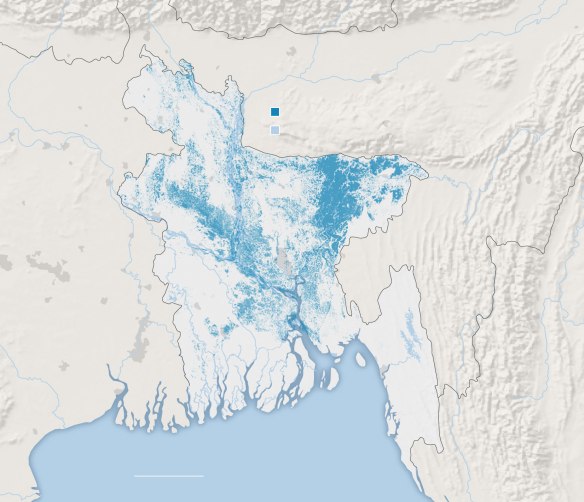
“Torrential rains have submerged at least a quarter of Bangladesh, washing away the few things that count as assets for some of the world’s poorest people — their goats and chickens, houses of mud and tin, sacks of rice stored for the lean season.
It is the latest calamity to strike the delta nation of 165 million people. Only two months ago, a cyclone pummeled the country’s southwest. Along the coast, a rising sea has swallowed entire villages. And while it’s too soon to ascertain what role climate change has played in these latest floods, Bangladesh is already witnessing a pattern of more severe and more frequent river flooding than in the past along the mighty Brahmaputra River, scientists say, and that is projected to worsen in the years ahead as climate change intensifies the rains.
“The suffering will go up,” said Sajedul Hasan, the humanitarian director of BRAC, an international development organization based in Bangladesh that is distributing food, cash and liquid soap to displaced people.”
“This is one of the most striking inequities of the modern era. Those who are least responsible for polluting Earth’s atmosphere are among those most hurt by its consequences. The average American is responsible for 33 times more planet-warming carbon dioxide than the average Bangladeshi.
This chasm has bedeviled diplomacy for a generation, and it is once again in stark relief as the coronavirus pandemic upends the global economy and threatens to push the world’s most vulnerable people deeper into ruin.
An estimated 24 to 37 percent of the country’s landmass is submerged, according to government estimates and satellite data By Tuesday, according to the most recent figures available, nearly a million homes were inundated and 4.7 million people were affected. At least 54 have died, most of them children.
The current floods, which are a result of intense rains upstream on the Brahmaputra, could last through the middle of August. Until then, Taijul Islam, a 30-year-old sharecropper whose house has washed away, will have to camp out in a makeshift bamboo shelter on slightly higher ground. At least he was able to salvage the tin sheet that was once the roof of his house. Without it, he said, his extended family of nine would be exposed to the elements.
Mr. Islam’s predicament is multiplied by the millions among those on the front lines of climate change. Vanuatu is literally sinking into the Pacific. Pastoralists in the Horn of Africa are being pushed to the edge of survival by back-to-back droughts. In the megacity of Mumbai, the rains come in terrifying cloudbursts.”

David Lindsay:
Bravo. Here is one of many good comments:
Idaho
Here we go again. The US with 5% of the worlds population uses 25% of its resources. The US is number one in co2 emissions per capita and is only exceeded by China, with 4x our population in total emissions. This, however, is not the whole story. In 1970 when Bangladesh became a country it had a population of ~65 million. It is now ~165 million. While they do not contribute individually or collectively anywhere near as much as a western person or country to climate change that kind of growth in one lifetime has disastrous effects on the local environment and how people live. More land is needed for food production, housing, clothing and on and on, and people spread out to previously uninhabited areas, (the environment always pays for human numbers and activity) increasing the damage when things like flooding happen. In the US a similar effect is found. In 1970 the US had ~205 million people with a per capita co2 emissions of ~23 tons each. In 2020 the US has ~330 million people with co2 emissions of ~16 tons each (a 25% reduction). Population growth has completely wiped out all the gains of reducing our per capita co2 emissions. The point of this? Without addressing population growth both in the west and in every other country, nothing will be achieved. The effect of humans on the environment is simple. Number of people x lifestyle = effects. Both sides of the equation have to be addressed everywhere to have any lasting effect.
